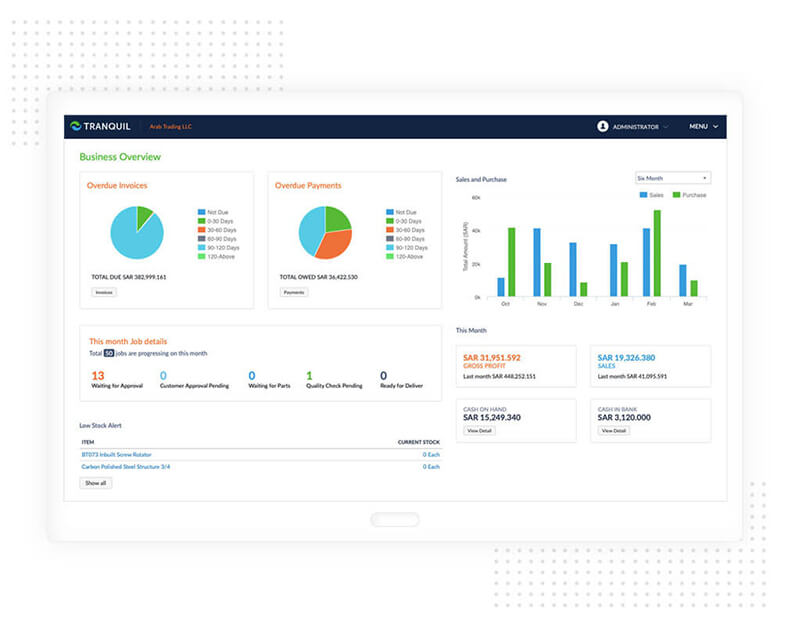
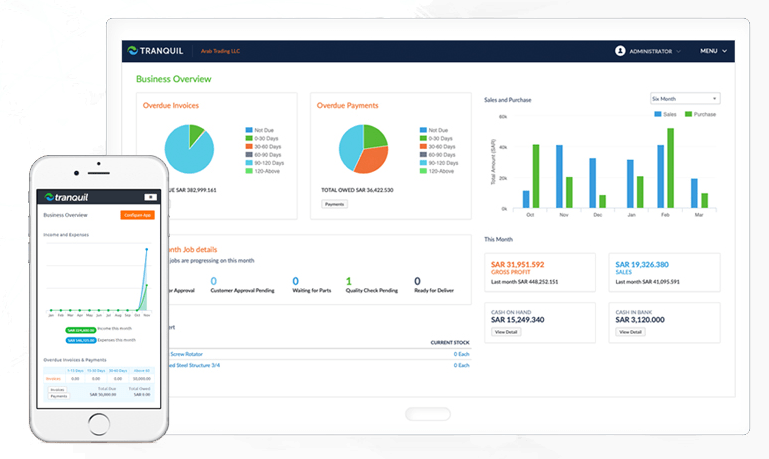
Tranquil Cloud ERP Job tracking option with variable employee pay rates allows you to know exactly how much you’re paying for each job.

Control of your quotes, jobs, invoices, payments and more. Tranquil Cloud ERP is built to simplify service, project and maintenance management.

Keep track of your Inventory and Warehouse locations with intelligent inventory software built for trade contractors.